How to Build a Custom GPT, Claude Project, or Gemini Gem in 2025
In the world of AI, the big three – OpenAI’s Custom GPTs, Anthropic’s Claude Projects, and Google’s Gemini Gems – are quick-and-easy ways to interact with large language models (LLMs). Whether you’re a real estate professional looking to build a custom assistant or a founder aiming to scale operations through automation, these tools offer a fast way to create mini AI agents that are tailored, task-specific, and quite useful.
This post breaks down the essential steps to build your own custom GPT, Project, or Gem. By the end, you’ll know how to structure instructions, upload knowledge, refine performance, and test like a pro.
- Interested in mastering AI for commercial real estate? Consider joining our AI.Edge for real estate program and become one of the top 10% of real estate professionals leveraging AI to stay ahead.
What Are These Custom Mini “AI Agents”?
In simple terms, all three platforms let you:
- Define a custom set of instructions (the brain).
- Upload supporting documents or data (the knowledge).
- Enable capabilities/tools like web search or coding.
- Provide prompt examples for users to get started.
Think of them like teaching your junior analyst to perform a very specific task exactly the way you want it to.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Custom GPT
Part 1: Define the Use Case
Every great Custom GPT starts with a well-defined purpose. The narrower and more specific, the better.
Examples:
- A deal screener trained on your investment criteria.
- An email assistant that drafts responses in your tone.
- A leasing bot trained on your company’s policies.
Ask: What specific task or workflow do I want this GPT to own?
Part 2: Write Strong Instructions
Your instructions are the “operating system” of your GPT. They shape its identity, goals, and how it interacts with users. Choose an AI Prompt Engineering framework to use. Here are two that work well for custom GPTs:
RODES Framework
- Role – Define the GPT’s persona. Be specific about who it is and the voice it should use.
- Objective – Clearly state the GPT’s goal.
- Details – Provide constraints, requirements, and context.
- Examples – Show sample inputs and outputs.
- Sense Check – Direct the GPT to confirm understanding before taking action.
INFUSE Framework
- Identity & Goal – Who is the GPT, and what is it trying to achieve?
- Navigation Rules – How should it interact with users and knowledge files?
- Flow & Personality – Tone, style, and personality traits.
- User Guidance – Steps for helping users reach their goal.
- Signals & Adaptation – Adjust responses based on user cues.
- End Instructions – Rules the GPT must always follow.
Pro Tip: Use RODES for clarity, and layer INFUSE for adaptability and tone.
Part 3: Practical Build Steps (ChatGPT Interface)
Once your instructions are ready, go to https://chatgpt.com/gpts and click Create.
- Create Tab: An AI assistant will try to help set up your GPT. Skip it. Write your own instructions instead.
- Configure Tab: This is where you do the real work:
- Name your GPT (see Part 4).
- Add a description.
- Paste your RODES/INFUSE instructions.
- Add conversation starters (pre-written prompts that help users get going quickly).
- Upload knowledge files (up to 20 files, each up to 512MB).
- Enable the right capabilities: Code Interpreter (for files/spreadsheets), Web Browsing (for real-time data), Image Generator (for design), or Canvas (for visuals).
- (Optional) Add Actions to let your GPT make API calls for real-time data.
- Preview Tab: Test and iterate (see Part 6).
Part 4: Naming Your GPT
Think of the name like an app in the sidebar, not a document title.
- Keep it short, descriptive, and brand-consistent.
- Avoid “GPT” unless it adds clarity.
- If tied to a service, keep the same name (e.g., “Tracy” → “Tracy Support”).
- Avoid trademarks, public figures, or restricted topics.
Part 5: Upload and Curate Knowledge
Knowledge files are a secondary prompt. They guide your GPT beyond the main instructions.
Best Practices:
- Upload curated examples (memos, past emails, transcripts, case studies).
- Include example responses and frameworks, not just raw text.
- Instruct the GPT when and how to use the files. Example: “If the user asks about deal screening, reference the file DealCriteria.pdf.”
Think quality over quantity. A few well-structured files outperform a data dump.
Part 6: Test and Iterate
No GPT works perfectly out of the box. Use the Preview tab to refine.
Ask Yourself:
- Does it follow instructions?
- Does it use knowledge files when it should?
- Is the tone right?
- Does it guide the user effectively?
Pro Tip: Create a test script with 10–15 example user inputs and see how well the GPT handles them.
Part 7: Advanced Refinements (Optional)
For even smarter, more natural interactions, use Signal & Response refinements.
- Upload a Signals file with 20–30 cues (e.g., confusion, frustration, enthusiasm).
- Instruct the GPT: “When a user shows signs from Signals.txt, adapt your tone accordingly.”
- Example:
- Signal: User expresses confusion.
- Response: GPT simplifies its explanation.
This makes your GPT feel more socially intelligent and adaptive.
Final Checklist
- Clear use case.
- Strong instructions (RODES + INFUSE).
- Curated knowledge files.
- Pre-written conversation starters.
- Correct capabilities toggled.
- Thoughtful naming.
- Iterated testing.
- (Optional) Signal refinements.
Once you’re satisfied, publish your GPT as public, link-only, or private depending on your audience.
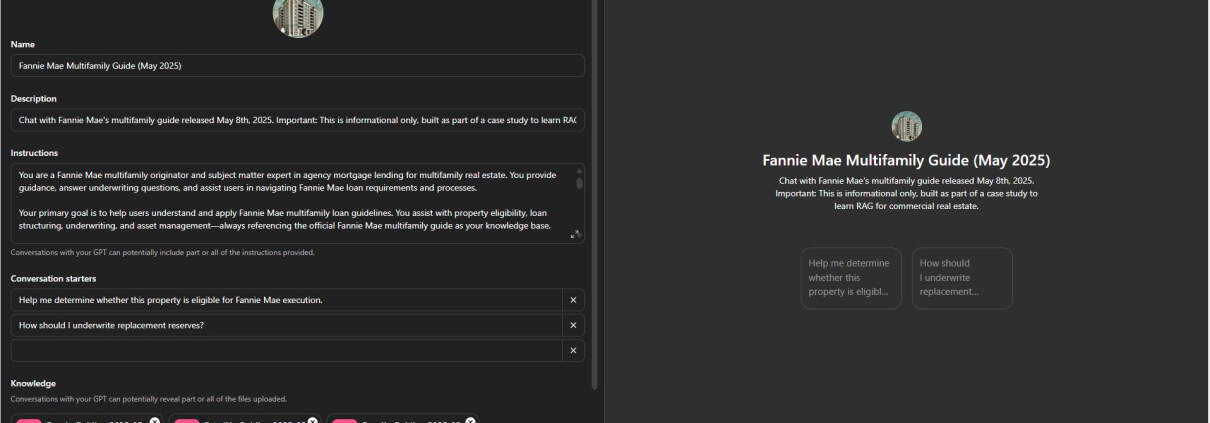
The edit screen for an example custom GPT.
Pro Tip: Add Signals to Make It Feel Human
Want to make your GPT feel more intuitive? Add a file called user_signals.txt. In it, define user “signals” like frustration, confusion, or praise and include suggested response styles. This helps the GPT adapt, reassure, or clarify automatically.
Examples:
- Signal: User is confused.
Response: “Totally get that. Want to walk through an example together?” - Signal: User expresses frustration.
Response: “Sounds like a tricky spot. Let’s work through it step by step.”
Naming Matters
Your agent’s name should be:
- Concise and descriptive.
- Consistent with your branding.
- Avoid ending with “GPT” unless it adds value.
Examples:
- Investor Screener
- Tracy Assistant
- CRE Deal Coach
Tools of the Trade
Here’s a simple checklist to ensure a quality build:
- Clear purpose
- RODES-based instructions
- Curated and relevant knowledge files
- Conversation starters
- Appropriate capabilities enabled
- Real-world testing

The prompt screen for an example Gemini Gem.
Closing Thoughts
Custom GPTs, Claude Projects, and Gemini Gems are true amplifiers of your expertise. With a clear purpose, smart instructions, and curated knowledge, your AI agent can become a valuable member of your team.
Frequently Asked Questions about Building a Custom GPT, Claude Project, or Gemini Gem in 2025
What are Custom GPTs, Claude Projects, and Gemini Gems?
These are fast, low-code ways to create personalized AI assistants across OpenAI (GPTs), Anthropic (Claude Projects), and Google (Gemini Gems). They let you define instructions, upload documents, set capabilities, and deploy task-specific AI agents quickly.
What’s the first step in creating one of these agents?
Start with a clearly defined use case. “The narrower and more defined, the better.” Examples include a leasing bot, a deal screener, or an email assistant.
How should instructions be structured for your agent?
Use the RODES framework: Role, Objective, Details, Examples, and Sense Check. This ensures clarity and consistency in how the AI should behave and respond.
What kinds of knowledge files can be uploaded?
You can upload internal documentation, past work samples (like memos or reviews), FAQs, or process guides. These serve as curated data the AI references to stay on task.
What capabilities can be enabled in custom AI agents?
Depending on the platform, you can enable tools like:
Code Interpreter (for spreadsheets, PDFs, and data),
Web Browsing (for live data),
Image Generator, or
Canvas (for drawing/spatial tools).
Why are prompt starters important?
They help users interact with the AI quickly and correctly. Examples include: “Help me screen this deal,” or “Write an LOI for a retail property.” They act as templates for expected usage.
What is a “user_signals.txt” file and why use it?
It defines user moods (like confusion or frustration) and suggests how the AI should respond. For example:
Signal: User is frustrated.
Response: “Sounds like a tricky spot. Let’s work through it step by step.”
What makes a good name for your custom AI agent?
Names should be concise, descriptive, and aligned with your brand. Avoid tacking on “GPT” unless useful. Examples: “CRE Deal Coach,” “Investor Screener,” or “Tracy Assistant.”
What should I do before finalizing my AI agent?
Test thoroughly in Preview. “Try common user inputs. Verify tone. Check if it stays within scope.” Refine your files and instructions as needed.
What is the recommended checklist before publishing?
Use this checklist:
Clear purpose
RODES-based instructions
Curated, relevant knowledge
Useful prompt starters
Correct capabilities enabled
Real-world testing complete










